Script Writer
| Function Syntax | WScript |
| Current Version | 1.2 |
| Download | ScriptWriterV1-2.lsp |
| View HTML Version | ScriptWriterV1-2.html |
| Compatible with AutoCAD for Mac? | No |
| Compatible with AutoCAD LT? | No |
| Donate |
Program Description
The aim of this program is to reduce the construction of an AutoCAD Script to a single line.
The program assumes the user is conversant in writing scripts for AutoCAD, if not, refer to my tutorial: An Introduction to Script Writing.
This program is designed to greatly reduce the time involved in writing scripts as an alternative to the usual scripting programs available.
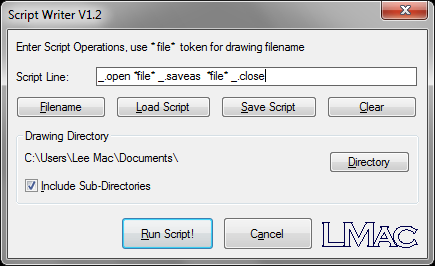
Upon starting the program, the user is presented with a dialog interface. Near the top, the user may enter a Script Line - this is the list of commands that will be performed on each drawing in the selected directory (and subdirectories).
The user only needs to write the first line of the script, which will be performed on every drawing in the selected directory; this is achieved through the use of a special token string to represent the drawing filename in the line of script operations.
Example
Consider the example from my script writing tutorial:
_.open "C:\My Folder\Drawing1.dwg" _.circle 0,0,0 5 _.save _Y _.close _.open "C:\My Folder\Drawing2.dwg" _.circle 0,0,0 5 _.save _Y _.close _.open "C:\My Folder\Drawing3.dwg" _.circle 0,0,0 5 _.save _Y _.close
To avoid having to construct the whole script, we can convert the first line for use with the Script Writer program, as follows:
_.open *file* _.circle 0,0,0 5 _.save _Y _.close
The program will then replace this token with the filename of each drawing in the selected directory (and subdirectories), and subsequently run the constructed script.
Additional Controls
The programs provides additional buttons to save even more time in writing the script line operations: the user may quickly insert the *file* token or clear the existing line by pressing the Filename and Clear buttons respectively.
Scripts may also be saved for later use, or existing scripts may be loaded into the program using the Load / Save buttons.
Preview
Instructions for Running
Please refer to How to Run an AutoLISP Program.
